Configuring Backtrace for Unity
Configure Backtrace for your Unity project. This page defines the configuration settings, classes, and methods available with the Backtrace Unity SDK.
Usage
//Read from manager BacktraceClient instance
var backtraceClient = GameObject.Find("_Manager").GetComponent<BacktraceClient>();
try
{
//throw exception here
}
catch(Exception exception)
{
var report = new BacktraceReport(exception);
backtraceClient.Send(report);
}
After you've setup the Backtrace client and database configuration, you can retrieve database and client instances by using GameObject, then use a try/catch statement to throw an exception and start sending reports.
Configuration Settings
The configuration settings for the Backtrace client and database are defined by the Backtrace Configuration file in the Assets folder of your Unity project. It's recommended to change the configuration settings for the Backtrace client and database in the Unity Inspector:
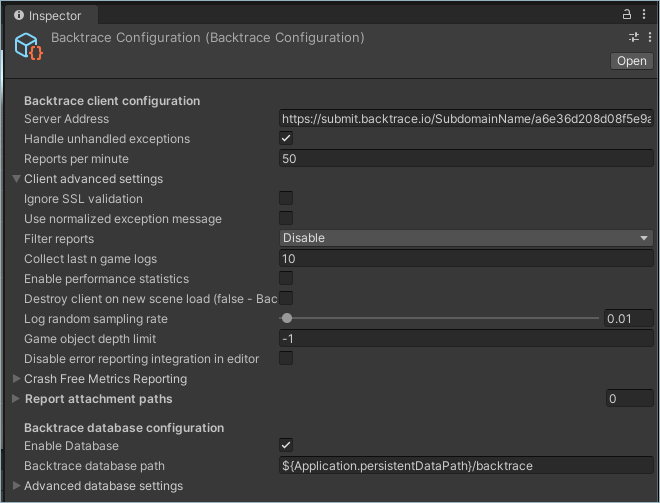
Alternatively, you can also specify the configuration settings in your C# project.
Backtrace Client
| Setting | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Server Address | The server address (submission URL) is required to submit exceptions from your Unity project to your Backtrace instance. The Server Address must be in the following format: https://submit.backtrace.io/{subdomain}/{submission-token}/json. | String | |
| Handle unhandled exceptions | Handles unhandled exceptions that are not captured by try/catch statements. | Boolean | True |
| Reports per minute | Limits the number of reports the client will send per minute.
BacktraceClient.Send and BacktraceClient.SendAsync methods will return 'false'. | Number | 50 |
| Ignore SSL validation | By default, Unity validates SSL certificates. If you don't want to validate SSL certificates, set the value to 'true'. | Boolean | False |
Backtrace Database
| Setting | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable Database | Enables an offline database to store reports locally. This is a requirement for native crash reports to be sent. | Boolean | False |
| Backtrace database path | Specifies the absolute path that the local database will use to store reports for your game or app. Note that the Backtrace database will remove all existing files in the database directory when the client is first initialized. You can use interpolated strings such as ${Application.persistentDataPath}/backtrace/database. | String | |
| Client-Side deduplication | Aggregates duplicated reports. The available options are:
| Enum | Disable |
| Attach Unity Player.log | Attaches the Unity player log file to the Backtrace report. Available only for Windows and MacOS. | Boolean | False |
| Auto send mode | Sends reports to the server based on the retry settings described below. If the value is set to 'False', you can use the Flush or Send methods as an alternative. | Boolean | True |
| Create database directory | Creates the offline database directory if the provided path doesn't exist. | Boolean | True |
| Attach screenshot | Generates a screenshot and creates an attachment of the frame when an exception occurs in a game scene. | Boolean | False |
| Maximum number of records | The maximum number of reports stored in the offline database. When the limit is reached, the oldest reports are removed. If the value is equal to '0', then no limit is set. | Number | 8 |
| Maximum database size (mb) | The maximum database size in MB. When the limit is reached, the oldest reports are removed. If the value is equal to '0', then no limit is set. (Managed reports only) | Number | 0 |
| Retry interval | The amount of time (in seconds) to wait between retries if the database is unable to send a report. | Number | 60 |
| Maximum retries | The maximum number of retries to attempt if the database is unable to send a report. | Number | 3 |
| Retry order (FIFO/LIFO) | The order in which reports are sent to the Backtrace server:
| Enum | Stack |
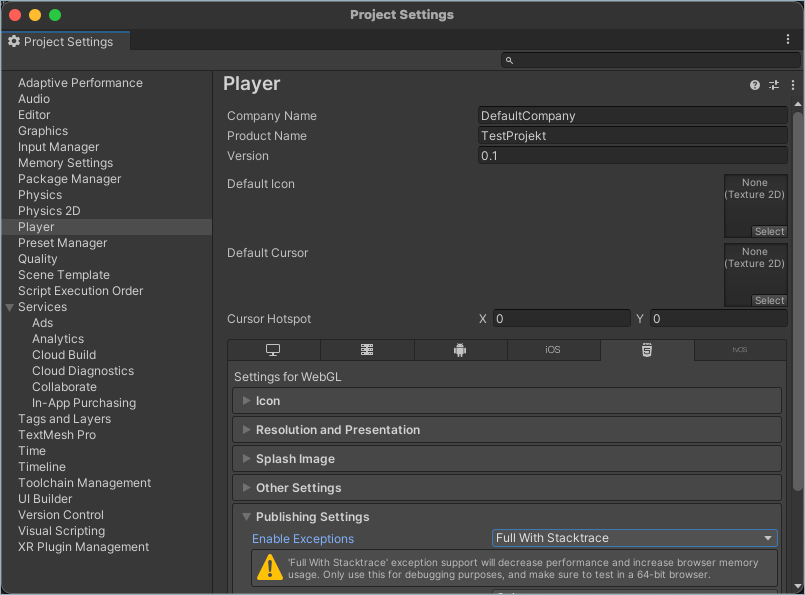
Enable Stack Traces for WebGL
To enable stack traces for WebGL, in your Unity project's Player Settings, under Publishing Settings, set Enable Exceptions to 'Full With Stacktrace'.
Advanced Client Settings
| Setting | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Use normalized exception message | Generates a fingerprint with a normalized exception message if an exception doesn't have a stack trace. | Boolean | False |
| Send unhandled native game crashes on startup | Sends native crashes when the game or app starts. Available only for Windows. | Boolean | True |
| Filter reports | Ignores managed error reports based on error type:
| Enum | Disable |
| Collect last n game logs | Collects last n number of logs generated in the game. | Number | 10 |
| Enable performance statistics | Allows the Backtrace client to measure execution time and include performance information as report attributes. | Boolean | False |
| Destroy client on new scene load | Removes the Backtrace client component when loading a new game scene. By default, the Backtrace client will be available in every game scene. | Boolean | False |
| Log random sampling rate | The rate at which random sample reports for DebugLog.error messages are sent to Backtrace. By default, 1% of the DebugLog.error messages will be sent to Backtrace. To send all DebugLog.error messages to Backtrace, set the value to '1'. | Decimal | 0.01 |
| Game object depth limit | Filters the number of GameObject children in Backtrace reports. | Number | -1 |
| Disable error reporting integration in editor | Ignores errors encountered while the project is running in the Unity Editor and only reports errors encountered in a build. | Boolean | False |
Crash Free Metrics Reporting
Once enabled, unique application launches and unique player identifiers (default: guid) will be submitted to Backtrace so you can get an overview of how many errors, hangs, crashes, and memory problems occur compared to all active users for a given platform, version, and more.
This functionality is supported on all platforms except WebGL.
| Setting | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable crash free metrics reporting | Enables metrics such as crash free users and crash free sessions. | Boolean | True |
| Auto send interval in min | Indicates how often crash free metrics are sent to Backtrace. By default, session events are sent on application startup, when the game ends, and every 30 minutes while the game is running. | Number | 30 |
You can enable crash free metrics at runtime with backtraceClient.EnableMetrics().
You can also add custom metrics groups and attributes with backtraceClient.Instance.Metrics.AddSummedEvent.
Capturing Native Crashes
- Android
- iOS
- Windows
system.memory.freesystem.memory.swap.freesystem.memory.vmalloc.totalsched.cs.involuntarysched.cs.voluntary
| Setting | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capture native crashes | Captures and symbolicates stack traces for native crashes. A crash report is generated, stored locally, and uploaded upon next game start. This requires "Enable Database" to also be true. | Boolean | True |
| Capture ANR (Application not responding) | Generates an error report whenever an app hangs for more than 5 seconds. The error.type for these reports will be Hang. | Boolean | True |
| Send Out of Memory exceptions to Backtrace | Detects low memory conditions. If the app crashes due to a memory condition, a crash report will be submitted to Backtrace with the memory.warning and memory.warning.date attributes. | Boolean | False |
| Enable client-side unwinding | Enables callstack unwinding. If you're unable to upload all debug symbols for your app, you can use this setting to get debug information. Available only for supported versions of Android (NDK 19; Unity 2019+). You can also enable this setting via the BacktraceConfiguration object and the .ClientSideUnwinding = true; option. | Boolean | False |
| Symbols upload token | Required to automatically upload debug symbols to Backtrace. To generate a symbol upload token, in Backtrace go to Project Settings > Symbols > Access tokens > and select + to generate a new token. | String |
ProGuard Rules
ProGuard obfuscation prevents the reflection used to invoke Java code from the Unity bridge. The ProGuard symbolication id must be passed to BacktraceClient, and additional ProGuard rules must be added to allow Backtrace to identify Java classes.Symbolication id is a UUID identifier created by the user. The same identifier value must be sent when uploading the source map and must be accessible in the game's runtime environment.
Please follow this guide to enable ProGuard, and add the following:
- Pass your ProGuard symbolication id to BacktraceClient:
var backtraceClient = GameObject.Find("manager name").GetComponent<BacktraceClient>();
var symbolicationId = "f6c3e8d4-8626-4051-94ec-53e6daccce25";
backtraceClient.UseProguard(symbolicationId); - Use these rules in proguard_rules.pro:
-keep class backtraceio.unity.* { *; }
-keep class backtraceio.library.**.* { *; }
Uploading Debug Symbols
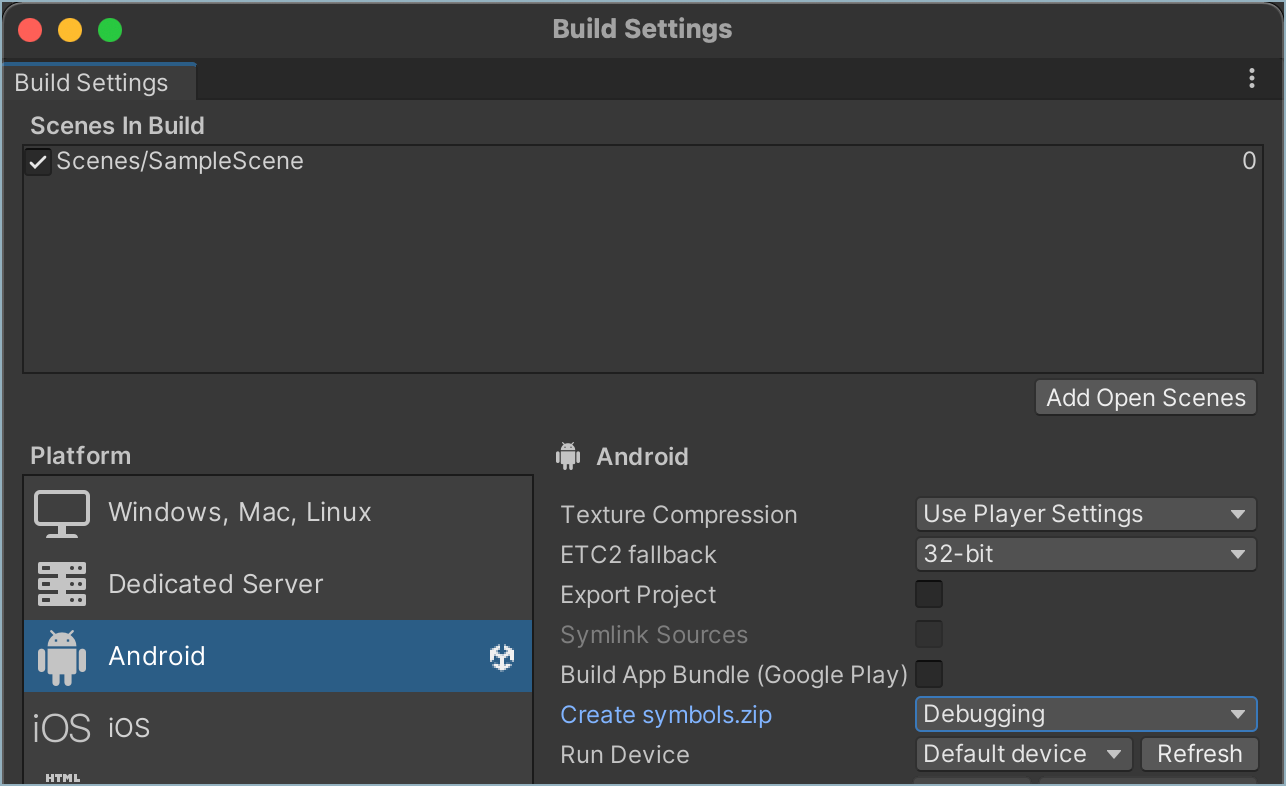
You can configure the Backtrace client to automatically upload debug symbols in IL2CPP builds for Android apps.To enable automatic upload of debug symbols, in your Unity project's Android settings:- In the Build Settings, set Create symbols.zip to 'Debugging'.
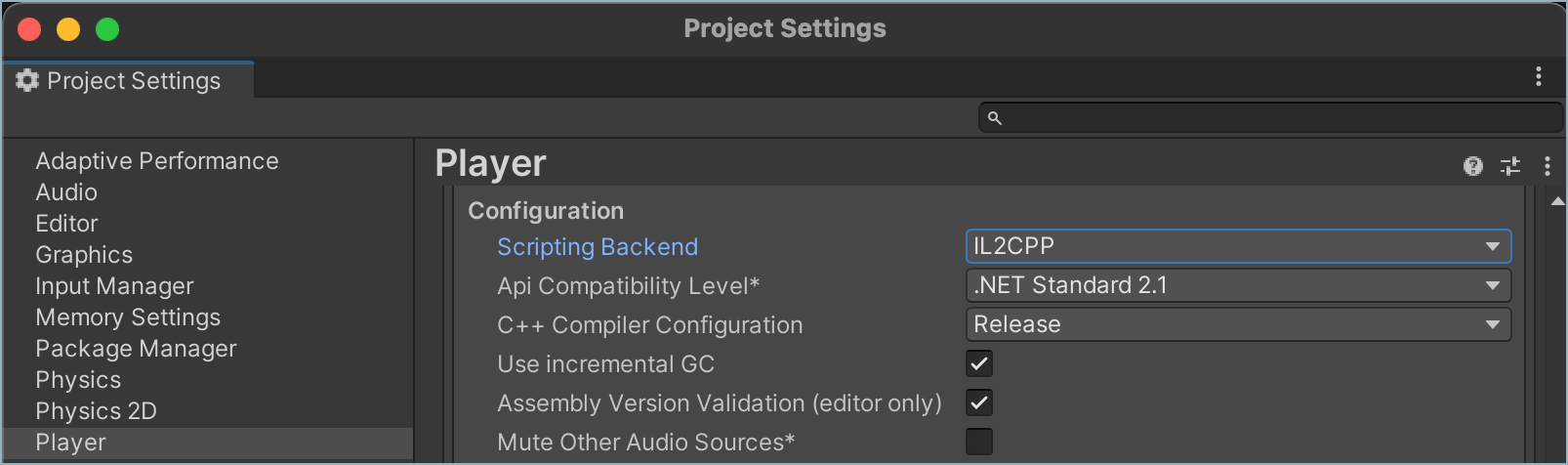
- In the Player Settings, under Configuration (Other Settings), set Scripting Backend to 'IL2CPP'.
system.memory.freesystem.memory.swap.usedsystem.memory.totalsystem.memory.activesystem.memory.inactive
| Setting | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capture native crashes | Captures and symbolicates stack traces for native crashes. A crash report is generated, stored locally, and uploaded upon next game start. | Boolean | True |
| Capture ANR (Application not responding) | Generates an error report whenever an app does not respond or hangs for more than 5 seconds. The error.type for these reports will be Hang. | Boolean | True |
| Send Out of Memory exceptions to Backtrace | Captures snapshots of the app's state when there is a low memory condition. If the app crashes due to a low memory condition, the information is sent to Backtrace. Snapshots are captured every 2 minutes as long as the low memory condition persists. | Boolean | False |
| Enable client-side unwinding | Enables callstack unwinding. If you're unable to upload all debug symbols for your app, you can use this setting to get debug information. You can also enable this setting via the BacktraceConfiguration object and the .ClientSideUnwinding = true; option. | Boolean | False |
Unity's CrashReport API might prevent the Backtrace client from sending crashes. To allow Backtrace to capture native crashes, in your Unity project's Player Settings for iOS, under Debugging and crash reporting, make sure that Enable CrashReport API is set to 'False'.
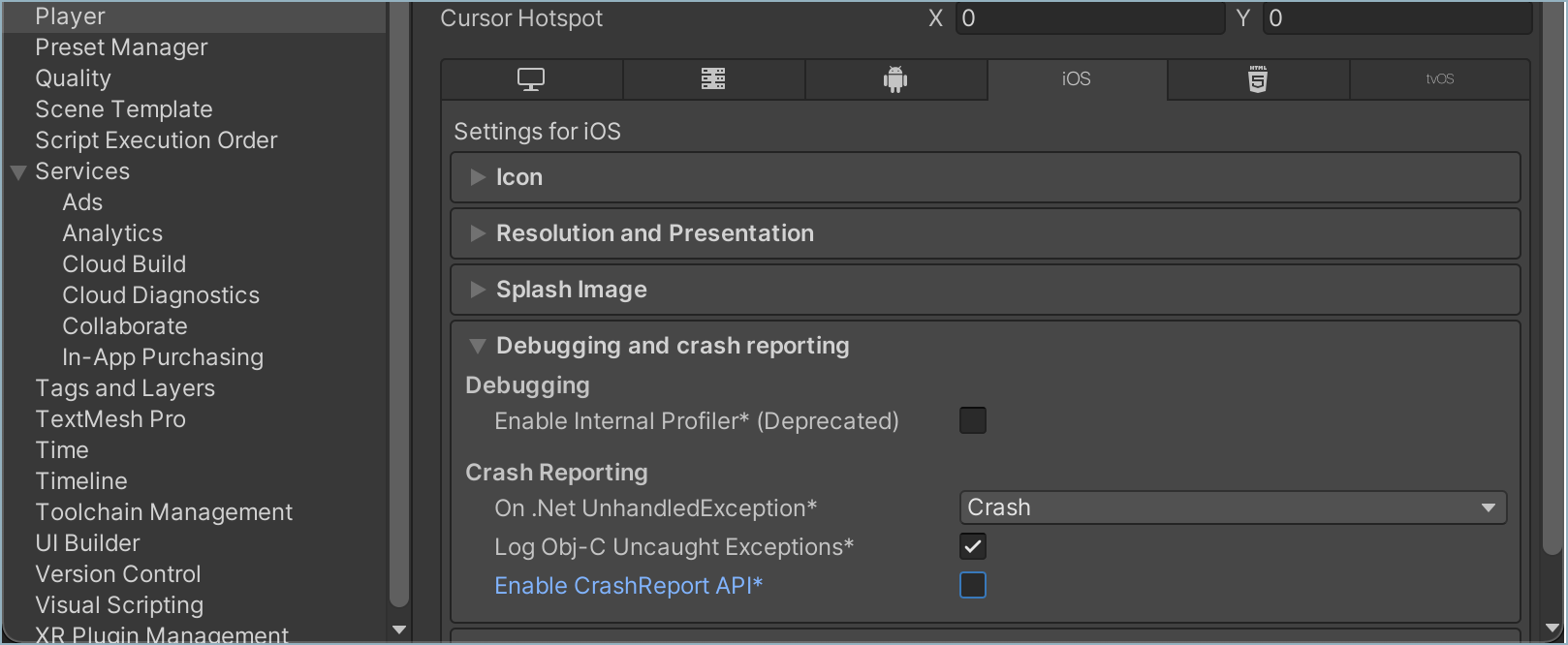
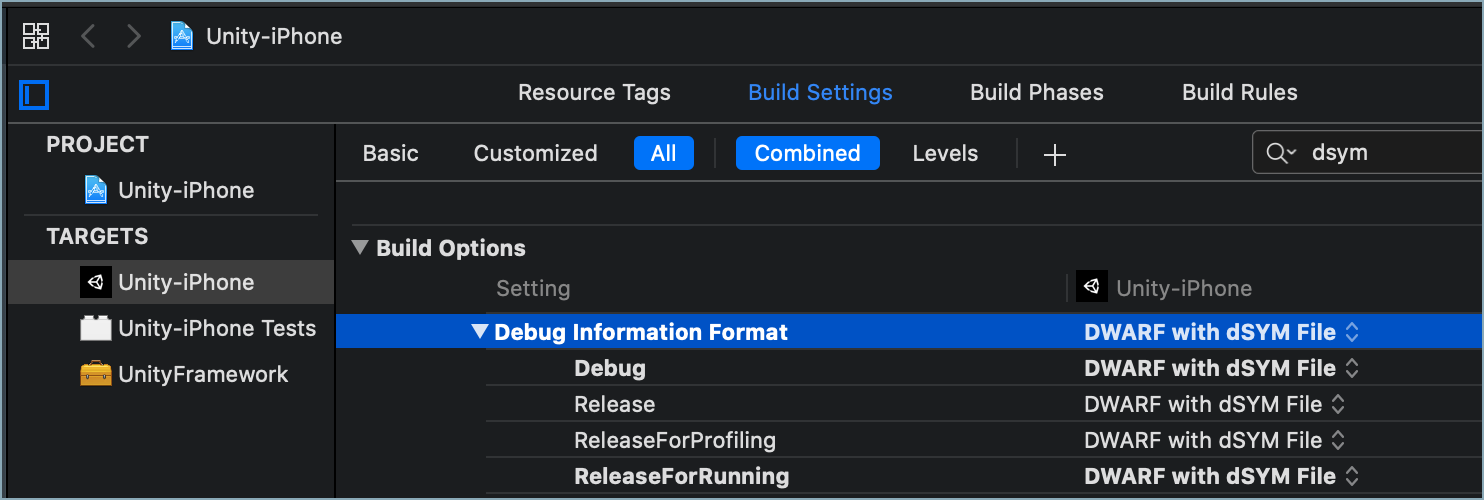
Uploading Debug Symbols
When building your iOS game in Xcode, make sure to configure the build settings to generate dSYM files for any build that you want to debug with Backtrace. By default, Xcode may only generate DWARF files.To generate debug symbols in dSYM format:- In Xcode, go to your project target's Build Settings.
- Under Build Options, set Debug Information Format to DWARF with dSYM File.
 You can find the dSYM files in the Build folder for your project (
You can find the dSYM files in the Build folder for your project (.../Build/Products/<build target folder>), which you can then compress into a .zip file and upload to Backtrace.For more information about debug symbols, see Symbolication.| Setting | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minidump type | The type of memory information to capture from Windows minidump reports. | Enum | None |
| Capture native crashes | Captures stack traces for native crashes. A crash report is generated, stored locally, and uploaded upon next game start. | Boolean | True |
| Capture ANR (Application not responding) | Generates a hang report whenever an app hangs for more than 5 seconds. The error.type for these reports will be Hang. | Boolean | True |
Logging Breadcrumbs
| Setting | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable breadcrumbs support | Logs breadcrumb events, such as the app going to a background process, logging messages, network connectivity lost, and more. By default, breadcrumbs are limited to 64kB and older events will automatically be removed. | Boolean | False |
| Breadcrumbs event type | Specifies which type of events to log. | Enum | Everything |
| Breadcrumbs log level | Specifies which log level severity to include. | Enum | Everything |
You can also add custom breadcrumb events, with information like "player completed a level" and sub attributes:
GetComponent<BacktraceClient>().Breadcrumbs.Info("Player Base Upgraded", new Dictionary<string, string>() {
{"base.name", "MtGox"},
{"base.level", "15"}
});
Advanced Configuration
backtraceApi
| CLASS | REQUIRED |
Class used to send diagnostic data in JSON format to the Backtrace endpoint, including asynchronous reports. backtraceApi is instantiated when the backtraceClient awake method is called.
backtraceClient
| CLASS | REQUIRED |
Class used to send backtraceReport to the Backtrace server by using backtraceApi. backtraceClient requires a Backtrace Configuration window.
This class inherits MonoBehavior functions.
//Read from manager BacktraceClient instance
var backtraceClient = GameObject.Find("manager name").GetComponent<BacktraceClient>();
//Set custom client attribute
backtraceClient["attribute"] = "attribute value";
//Read from manager BacktraceClient instance
var database = GameObject.Find("manager name").GetComponent<BacktraceDatabase>();
try{
//throw exception here
}
catch(Exception exception){
var report = new BacktraceReport(exception);
backtraceClient.Send(report);
}
backtraceClient.Initialize
| METHOD | REQUIRED |
Method used to initialize the Backtrace Unity SDK directly in the C# code of your Unity project.
var backtraceClient = BacktraceClient.Initialize(
url: serverUrl,
databasePath: "${Application.persistentDataPath}/sample/backtrace/path",
gameObjectName: "game-object-name",
attributes: attributes);
If you need to use more advanced configuration settings, the Initialize method accepts a BacktraceConfiguration scriptable object. For example:
var configuration = ScriptableObject.CreateInstance<BacktraceConfiguration>();
configuration.ServerUrl = serverUrl;
configuration.Enabled = true;
configuration.DatabasePath = "${Application.persistentDataPath}/sample/backtrace/path";
configuration.CreateDatabase = true;
configuration.Sampling = 0.002;
configuration.ClientSideUnwinding = true;
_backtraceClient = BacktraceClient.Initialize(
configuration,
gameObjectName: "game-object-name",
attributes: attributes);
backtraceClient.Instance.Metrics.AddSummedEvent
| METHOD | OPTIONAL |
Used to add custom metrics groups and attributes to capture your game or apps' stability.
For example, if you want to know details about the levels that a user has played in your game, you can add a "LevelsPlayed" event with the application.version and score attributes.
BacktraceClient.Instance.Metrics.AddSummedEvent("levels_played", new Dictionary<string, string>() {
{"application.version", BacktraceClient.Instance["application.version"]},
{"score", "" + score}
}
);
As another example, if you want to know how many minutes a user has played your game, you can add a "MinutesPlayed" event with the application.version and uname.sysname attributes.
private void Update()
{
timeElapsedSeconds += Time.deltaTime;
// Every second, add an event for this metric group
if (timeElapsedSeconds >= 60)
{
timeElapsedSeconds = 0;
// Generate your attribute values for the attributes you want linked
Dictionary<string,string> attributes = new Dictionary<string, string>()
{
{ "application.version", BacktraceClient.Instance["application.version"] },
{ "uname.sysname", BacktraceClient.Instance["uname.sysname"] },
{ "custom.field", "custom.value" },
};
// Add the summed event using the metric group name and attributes
BacktraceClient.Instance.Metrics.AddSummedEvent("MinutesPlayed", attributes);
}
}
The example above adds an event for this metric group to a queue, which will be sent based on the Auto send interval setting in the Backtrace Configuration in Unity.
You can adjust the frequency of that send process to suit your needs and/or manually send the events with BacktraceClient.Instance.Metrics.Send().
Adding multiple events with many linked attributes or sending the metrics events too frequently may affect the performance of your game or app and contribute a lot of data towards your Backtrace data storage limits.
backtraceClient.Refresh
| METHOD | OPTIONAL |
Method used to refresh and apply the configuration settings for the Backtrace client when you change the configuration dynamically. For example:
//Read from manager BacktraceClient instance
var backtraceClient = GameObject.Find("manager name").GetComponent<BacktraceClient>();
//Set custom client attribute
backtraceClient["attribute"] = "attribute value";
//Change configuration value
backtraceClient.configuration.DeduplicationStrategy = deduplicationStrategy;
//Refresh configuration
backtraceClient.Refresh();
backtraceClient.Send
| METHOD | REQUIRED |
Method used to send error reports to the Backtrace endpoint.
try
{
//throw exception here
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
var report = new BacktraceReport(
exception: exception,
attributes: new Dictionary<string, string>() { { "key", "value" } },
attachmentPaths: new List<string>() { @"file_path_1", @"file_path_2" }
);
backtraceClient.Send(report);
}
Custom Event Handlers
You can also add custom event handlers to the client. For example, you can use BeforeSend to trigger actions before the Send method:
//Add a custom event handler
backtraceClient.BeforeSend =
(Model.BacktraceData model) =>
{
var data = model;
//do something with the data, for example:
data.Attributes.Attributes.Add("eventAttribute", "EventAttributeValue");
if(data.Classifier == null || !data.Classifier.Any())
{
data.Attachments.Add("path to attachment");
}
return data;
};
BacktraceClient currently supports the following events:
BeforeSendOnClientReportLimitReachedOnServerResponseOnServerError
You can also use the backtraceReport class to customize the data included in the error reports sent by the backtraceClient.
backtraceClient.SkipReport
| SETTING | OPTIONAL |
If you want to ignore specific types of error reports, we recommend that you use the Filter reports settings in the Backtrace Configuration in the Unity Editor.
However, for more advanced use cases, you can use BacktraceClient.SkipReport to set the ReportFilterType. For example:
// Return 'true' to ignore a report,
// Return 'false' to handle the report and generate it for the error.
BacktraceClient.SkipReport = (ReportFilterType type, Exception e, string msg) =>
{
// ReportFilterType is one of None, Message, Exception, UnhandledException or Hang.
// It is also possible to filter based on the exception and exception message.
// Report hangs and crashes only.
return type != ReportFilterType.Hang && type != ReportFilterType.UnhandledException;
};
backtraceData
| CLASS | OPTIONAL |
Serializable class that holds the diagnostic data in JSON format to be sent to the backtrace endpoint via backtraceApi.
backtraceDatabase
| CLASS | REQUIRED |
Class that stores error report data in your local hard drive when reports fail to send due to network outages or server unavailability. backtraceDatabase will periodically try to resend reports cached in the database.
backtraceDatabase.Clear
| METHOD | OPTIONAL |
Clears all reports from the database without sending them to Backtrace server.
backtraceDatabase.Clear();
backtraceDatabase.Count
| METHOD | OPTIONAL |
Returns the number of reports stored in the database, including deduplicated reports.
backtraceDatabase.Count();
backtraceDatabase.Delete
| METHOD | OPTIONAL |
Removes a report stored in the database, including deduplicated reports.
backtraceDatabase.Delete();
backtraceDatabase.Flush
| METHOD | OPTIONAL |
Sends all reports to the Backtrace server then removes them from the database. This method is only needed to support the offline database when the Auto send mode is disabled.
The Flush method ignores client side deduplication and retry settings.
If the Send method fails, the database will no longer store data.
backtraceDatabase.Flush();
backtraceDatabase.Send
| METHOD | OPTIONAL |
Sends all reports to the Backtrace server, as defined by the client side deduplication and database retry settings. This method is only needed to support the offline database when the Auto send mode is disabled.
backtraceDatabase.Send();
backtraceReport
| CLASS | OPTIONAL |
Class that defines a single error report.
Attributes and Attachment Paths
You can submit custom attributes using the attributes parameter, or attach files by specifying an array of file paths with the attachmentPaths parameter. For example:
try
{
//throw exception here
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
var report = new BacktraceReport(
exception: exception,
attributes: new Dictionary<string, string>() { { "key", "value" } },
attachmentPaths: new List<string>() { @"file_path_1", @"file_path_2" }
);
backtraceClient.Send(report);
}
Fingerprint and Factor
You can use the Fingerprint and Factor properties to modify the client side deduplication strategy. The Fingerprint property changes the hash that is generated, while the Factor property changes how duplicated reports are aggregated.
Fingerprint values must be a valid SHA-256 string.
For example:
try
{
//throw exception here
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
var report = new BacktraceReport(...){
Fingerprint = "sha256 string",
Factor = exception.GetType().Name
};
...
}
The Backtrace client will send a single report when an exception occurs and maintain a count for every other time it occurs, which reduces the volume of reports that are generated and sent to Backtrace.
The count is reset when the offline database is cleared (usually when the reports are sent to the server) or if the game is closed before the reports are sent. A new single report is created the next time the exception occurs.
Information about aggregated reports is stored in backtraceDatabaseRecord. You can use the Hash property to verify the generated hash for the diagnostic data, and the Counter property to verify the count of duplicated reports.
reportWatcher
| CLASS | REQUIRED |
Class that validates send requests from backtraceApi to the Backtrace endpoint. If ReportPerMin is set to a value greater than '0' in the backtraceClient configuration, reportWatcher will limit the number of reports sent by the client.
Data Management
The Backtrace Unity SDK allows you to modify and remove data that the library collects when an exception occurs using the following methods:
backtraceClient.BeforeSend
| EVENT | OPTIONAL |
Triggers an event every time an exception in the managed environment occurs, which allows you to skip the report (by returning a null value) or to modify data that library collected before sending the report.
You can use the BeforeSend event to extend attributes or JSON object data based on data the application has at the time of exception.
//Read from manager BacktraceClient instance
var backtraceClient = GameObject.Find("manager name").GetComponent<BacktraceClient>();
// set beforeSend event
_backtraceClient.BeforeSend = (BacktraceData data) =>
{
data.Attributes.Attributes["my-dynamic-attribute"] = "value";
return data;
};
Annotation.EnvironmentVariables
| CLASS | OPTIONAL | STRING |
The Annotation class exposes the EnvironmentVariablesCache dictionary, which stores environment variables collected by the library. You can manipulate the data in this cache before the report is sent.
For example, you can use an annotation to replace the USERNAME environment variable with a random string, which will be used to create reports.
Annotations.EnvironmentVariablesCache["USERNAME"] = "%USERNAME%";
}
You can also use the BeforeSend event along with annotations for environment variables to edit collected diagnostic data.
client.BeforeSend = (BacktraceData data) =>
{
data.Annotation.EnvironmentVariables["USERNAME"] = "%USERNAME%";
return data;
}